- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 616-91-1
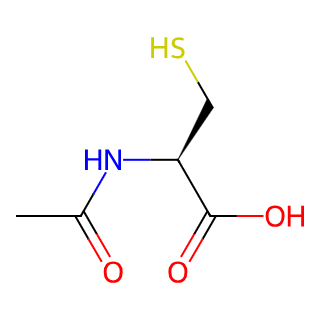



Acetylcysteine
Acetylcysteine (N-Acetyl-L-cysteine, N-Acetylcysteine) is an organic compound, primarily used as a mucolytic agent due to its strong ability to dissolve viscous mucus.
I. Basic Information
English Name: Acetylcysteine
Aliases: N-Acetyl-L-cysteine, N-Acetylcysteine
Chemical Formula: C5H9NO3S
Molecular Weight: 163.195
CAS Registry Number: 616-91-1
EINECS Registry Number: 210-498-3
II. Pharmacological Effects
Mucolytic Effect: The sulfhydryl group in Acetylcysteine can break the disulfide bonds in the glycoprotein polypeptide chains in mucus, thereby reducing mucus viscosity and making it easier to expectorate. It can also break the DNA fibers in purulent mucus, making it effective in dissolving both white and purulent mucus.
Antioxidant Effect: As a thiol compound, Acetylcysteine can directly react with free radicals and non-free radical oxidants, exhibiting significant antioxidant effects.
Anti-inflammatory Effect: Acetylcysteine can limit the release of cytokines during the initial stage of immune proliferation, reducing the levels of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in patients undergoing hemodialysis or with septic shock.
Other Effects: It also has effects such as dilating microvasculature and protecting DNA molecules. Clinically, it can be used for various indications such as COPD, bronchiectasis, and the treatment of acetaminophen poisoning.
III. Indications
Primarily used for respiratory diseases characterized by excessive viscous secretions, such as COPD and bronchiectasis.
Treatment of acetaminophen poisoning.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



