- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 27164-46-1



1. Basic Information
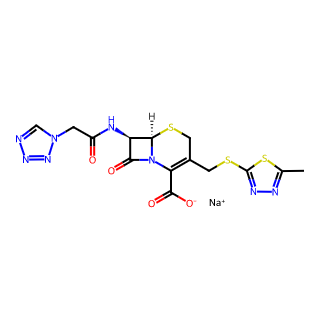
Product Name: Cefazolin Sodium
CAS Number: 27164-46-1
Molecular Formula: C14H13N8NaO4S3
Molecular Weight: 476.49
2. Physical Properties
Cefazolin Sodium appears as a white or off-white powder or crystalline powder, odorless with a slightly bitter taste.
It is highly soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, and practically insoluble in ethanol, acetone, chloroform, or benzene.
The aqueous solution of Cefazolin Sodium is transparent, colorless, or slightly yellowish and relatively stable. It may precipitate crystals upon cooling, which should be dissolved by warming.
3. Pharmacological Action
Cefazolin Sodium, as a first-generation cephalosporin, exhibits broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. It has good antibacterial effects against various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus (including β-lactamase-producing strains), Streptococcus (excluding Enterococcus), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus hemolyticus, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Enterobacter aerogenes.
The antibacterial mechanism of Cefazolin Sodium is primarily through inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls.
4. Indications
Cefazolin Sodium is indicated for the treatment of various infections caused by sensitive bacteria, including but not limited to:
Respiratory infections: such as otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.
Urinary tract infections.
Skin and soft tissue infections.
Bone and joint infections.
Sepsis.
Infective endocarditis.
Hepatobiliary system infections.
Infections of the eye, ear, nose, and throat.
Additionally, Cefazolin Sodium can be used as prophylactic medication before surgical procedures to reduce the incidence of postoperative infections.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



