- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 86393-32-0



Basic Information
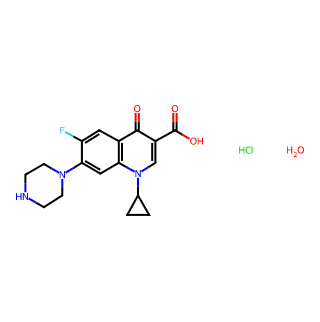
Product Name: Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Monohydrate
CAS Number: 86393-32-0
Molecular Formula: C17H21ClFN3O4
Molecular Weight: 385.82
Physical Properties
Appearance: White or slightly yellow crystalline powder
Solubility: Readily soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, and poorly soluble in ethanol. This property allows Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Monohydrate to have good solubility and bioavailability in aqueous environments.
Melting Point: 318-320°C
Boiling Point: 581.8°C at 760 mmHg
Flash Point: 305.6°C
Chemical Properties
Stability: Relatively stable under specific conditions (e.g., protected from light, sealed, and stored in a cool place). However, prolonged exposure to air, light, or high temperatures may lead to decomposition.
Reactivity: As an antibacterial agent, Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Monohydrate binds to specific enzymes (such as DNA gyrase) within bacterial cells, inhibiting their activity and thereby blocking bacterial DNA synthesis and replication, resulting in bacterial death.
Biological Properties
Antibacterial Spectrum: Possesses broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, particularly potent against Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Streptococci, and other pathogenic bacteria.
Pharmacological Action: As a third-generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent, Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Monohydrate exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase, which blocks bacterial DNA synthesis and replication, ultimately leading to bacterial death.
Uses and Precautions
Uses: Primarily used to treat various infections caused by susceptible bacteria, including respiratory infections, genitourinary infections, skin and soft tissue infections, etc.
Precautions: Use should follow medical advice, with attention paid to drug dosage, route of administration, and duration of treatment. Avoid adverse interactions with other medications. Monitor patients for adverse reactions, such as allergies or gastrointestinal discomfort, and discontinue medication and seek medical attention if necessary.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



