- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS Number: 56796-39-5



I. Basic Information
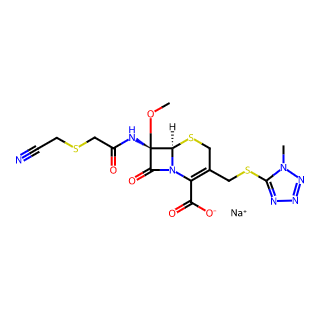
Product Name: Cefmetazole Sodium
CAS Number: 56796-39-5
Chemical Formula: C15H16N7NaO5S3 (Note: Variations in the chemical formula, such as C15H18N7NaO5S3, may exist due to different literature sources or preparation methods.)
Molecular Weight: 493.516 (or 495.52, depending on the specific chemical formula)
EINECS Number: 627-393-7
II. Physical Properties
Appearance: White to off-white powder (or white solid, depending on the source)
Melting Point: >130°C (dec.)
Density: 1.75 g/cm³
Solubility: Highly soluble in water (up to 50 mg/mL or 100 mg/mL, depending on the measurement conditions and methods), easily soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol, and practically insoluble in ether or dichloromethane.
Hygroscopicity: Slightly hygroscopic
III. Chemical Properties
Stability: Stable under appropriate storage conditions (e.g., low temperature, light protection, and sealing).
Mechanism of Action: By binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), it prevents the crosslinking of peptidoglycan, interfering with the biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to bacterial death.
IV. Pharmaceutical Characteristics
Antibacterial Activity: Cefmetazole sodium has antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and anaerobes. It is highly resistant to β-lactamases, thus exhibiting strong antibacterial activity against β-lactamase-producing bacteria similar to non-β-lactamase-producing sensitive bacteria.
Indications: It is used to treat infections caused by Cefmetazole sodium-sensitive organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus species, etc., including sepsis, respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, cholangitis, cholecystitis, peritonitis, and female genital infections.
Dosage and Administration: Generally, for adults, the daily dose is 12 grams (potency), administered in two divided doses via intravenous injection or infusion. For children, the daily dose is 25100 milligrams (potency) per kilogram of body weight, administered in two to four divided doses via intravenous injection or infusion. The specific dosage should be determined based on the patient's condition and medical guidance.
Adverse Reactions: Occasionally, allergic reaction symptoms such as urticaria, rash, and drug fever may occur. Rarely, anaphylactic shock may occur. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may also be seen. Temporary elevations in alanine aminotransferase levels and reports of hepatitis have been rarely observed.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



