- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS Number: 81103-11-9



Basic Information
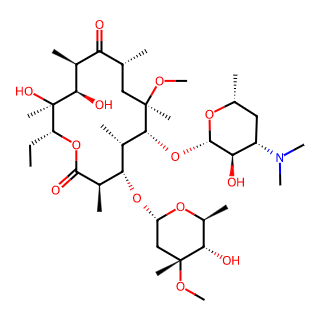
Product Name: Clarithromycin
Alternative Names: Erythromycin methylsuccinate, Klaricid, Clarithromycinum
CAS Number: 81103-11-9
Molecular Formula: C38H69NO13
Molecular Weight: 747.953 (or 747.96, slight variations may exist in different literature)
Physical Properties
Appearance and Physical State: White to off-white crystalline powder, odorless, bitter taste.
Density: 1.2±0.1 g/cm³
Melting Point: 217220ºC (obtained as colorless needle crystals from chloroform-isopropylether (1:2), decomposes); or from ethanol crystallization, melting point 222225ºC.
Boiling Point: 805.5±65.0 ºC at 760 mmHg
Flash Point: 440.9±34.3 ºC
Solubility: Easily soluble in chloroform or acetone, slightly soluble in ethanol, ether, or methanol, practically insoluble in water.
Chemical Properties and Pharmacological Effects
Clarithromycin belongs to the macrolide antibiotics, a derivative of erythromycin, obtained by replacing the OH group at position 6 of erythromycin A with OCH3.
It has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, Chlamydia, and Mycobacterium species.
Clarithromycin primarily binds to the 50S subunit of the 70S ribosomal system in bacteria, inhibiting peptide chain elongation and thus blocking bacterial protein synthesis, producing antibacterial effects.
Drug Characteristics and Uses
Clarithromycin is stable to gastric acid, with good oral absorption, high blood drug concentrations, and a long plasma half-life.
It is widely used to treat upper and lower respiratory tract infections, subcutaneous soft tissue infections, etc., effective for various infections in the respiratory, urinary, skin, ENT, and other systems.
Additionally, Clarithromycin is a CYP3A4 inhibitor, capable of affecting the metabolism of certain drugs.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



