- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 132539-06-1



Basic Chemical Information
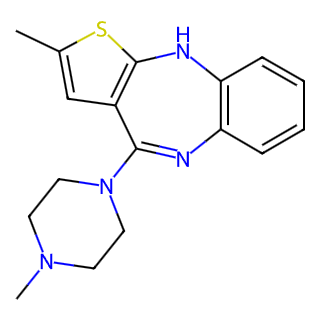
English Name: Olanzapine
Chemical Names: Thieno[2,3-b][1,5]benzodiazepine;
CAS Number: 132539-06-1
Molecular Formula: C17H20N4S
Molecular Weight: 312.44 g/mol
Pharmacological Action
Therapeutic Effects:
Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic medication used primarily to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It has been found effective in reducing symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and mood swings.
Mechanism of Action:
Olanzapine exerts its antipsychotic effects through a combination of actions on various neurotransmitter receptors in the brain:
Dopamine Receptor Antagonism: Olanzapine acts as an antagonist at D2 dopamine receptors, which helps to reduce the overactivity of dopamine that is associated with psychotic symptoms.
Serotonin Receptor Antagonism: It also antagonizes 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors, contributing to its effectiveness in reducing both the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia and stabilizing mood in bipolar disorder.
Muscarinic Receptor Antagonism: By antagonizing muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, olanzapine may also impact memory and cognitive functions, although this can lead to side effects such as dry mouth and constipation.
Histamine Receptor Antagonism: Olanzapine is an antagonist at H1 histamine receptors, which contributes to its sedative properties.
Alpha-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonism: Its antagonism of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors can lead to blood pressure effects and weight gain.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



