- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 100643-71-8
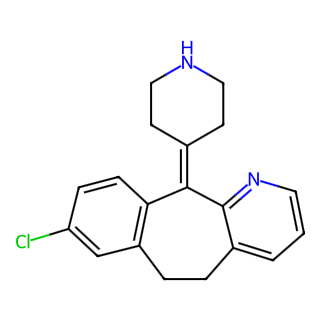



Desloratadine
Desloratadine is a commonly used anti-allergic medication belonging to the third-generation, long-acting, tricyclic histamine antagonists. It is primarily used to relieve the systemic and local symptoms of chronic idiopathic urticaria and perennial allergic rhinitis.
Basic Information
Chemical Name: 8-Chloro-6,11-dihydro-11-(4-piperidinylidene)-5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine
Molecular Formula: C19H19CIN2
Molecular Weight: 310.82
CAS Number: 100643-71-8
Pharmacological Action
Desloratadine is a non-sedating, long-acting tricyclic antihistamine that acts as an active metabolite of loratadine. It selectively antagonizes peripheral H1 receptors, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis or chronic idiopathic urticaria. In vitro studies have shown that desloratadine inhibits the release of histamine from human mast cells. Animal studies indicate that desloratadine has limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in weaker sedative effects compared to other antihistamines.
Efficacy
Antihistaminic Effect: Desloratadine inhibits the binding of histamine to H1 receptors, blocking histamine's effects on the body and thereby relieving symptoms such as nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, sneezing, and itchy eyes.
Antipruritic Effect: In allergic reactions, histamine released by tissues stimulates nerve endings, causing itching sensations. Desloratadine blocks nerve transmission, reducing itching sensations.
Anti-inflammatory and Anti-redness Effect: Allergic reactions can cause inflammatory responses in tissues, leading to skin and mucous membrane redness. Desloratadine, through its antihistaminic and anti-inflammatory effects, can alleviate inflammatory reactions and improve redness.
Sedative Effect: Although desloratadine has limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, it still possesses some sedative effects, which can help alleviate anxiety and tension caused by allergies and improve sleep quality.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



