- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 66085-59-4
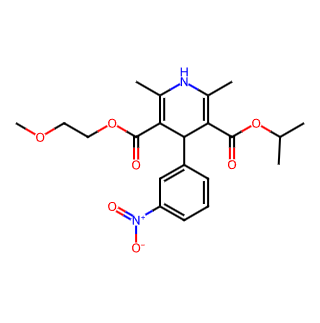



Basic Information
Chinese Name: 尼莫地平
English Name: Nimodipine
CAS Number: 66085-59-4
EINECS Number: 266-127-0
Molecular Formula: C21H26N2O7
Molecular Weight: 418.44
MDL Number: MFCD00153848
MOL File: 66085-59-4.mol
Synonyms
Chinese Synonyms: Nimodipine, (+/-)-4-(3-Nitrophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid methoxyethyl ester isopropyl ester, Lemodipine, Nimodipine (Nifedipine derivative), Nimotidine, etc.
English Synonyms: Nimodipine, 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3'-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid 2-methoxyethyl-1-methylethyl ester, etc.
Physical Properties
Appearance: Pale yellow crystalline powder, odorless, tasteless.
Solubility: Soluble in ethanol or acetone, insoluble in water.
Melting Point: 124-128°C
Boiling Point: 536.21°C (rough estimate)
Density: 1.3268 g/cm³ (rough estimate)
Refractive Index: 1.6500 (estimate)
Chemical Properties
Nimodipine is a new generation of 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (calcium antagonist). It inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells.
Pharmacological Effects
Easily crosses the blood-brain barrier to act on cerebral blood vessels and nerve cells.
Selectively dilates cerebral blood vessels without causing "steal phenomenon," increasing cerebral blood flow without affecting cerebral metabolism.
Antagonizes cerebral vasospasm caused by K+, 5-HT, arachidonic acid, hydrogen peroxide, TXA2, DGF2a, and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Has antidepressant effects and improves learning and memory functions.
Also reduces erythrocyte fragility, plasma viscosity, and inhibits platelet aggregation.
Indications
Primarily used for the prevention and treatment of ischemic neurological damage caused by cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage, as well as senile cerebral dysfunction, migraine, sudden deafness, etc.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



