- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS Number: 125317-39-7



Basic Information
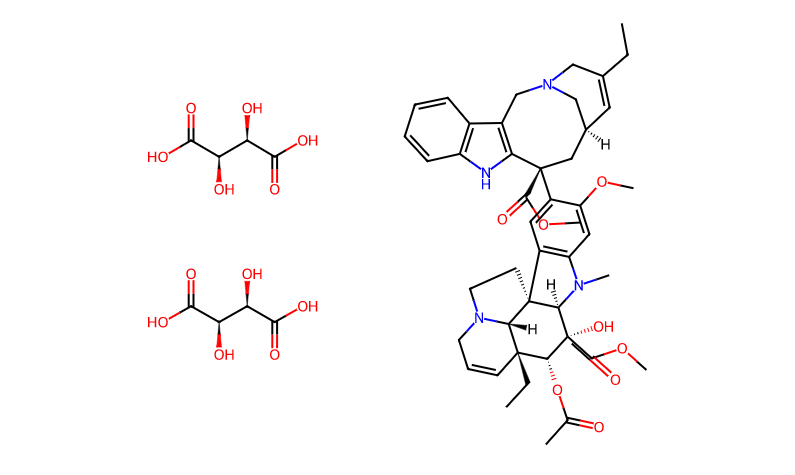
Product Name: Vinorelbine Tartrate
CAS Number: 125317-39-7
Chemical Formula: C53H66N4O20
Molecular Weight: 1079.11 g/mol
Appearance: White or almost white powder or crystalline solid
Chemical Properties
Structure: Vinorelbine tartrate has a specific chemical structure that includes a ditartrate salt form.
Solubility: It is soluble in water and can be formulated as an injectable solution.
Pharmacological Properties
Mechanism of Action: Vinorelbine tartrate is an inhibitor of cell division, acting directly on the dynamic balance of tubulin/microtubules. It inhibits the polymerization of tubulin and causes the disintegration of microtubules during the mitotic phase. By blocking the mitotic division of G2 and M phase cells, it leads to the death of cells entering the interphase or post-mitotic phase.
Antitumor Activity: Vinorelbine tartrate demonstrates antitumor activity against a variety of cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, metastatic breast cancer, refractory lymphoma, ovarian cancer, and head and neck tumors.
Applications
Therapeutic Use: Vinorelbine tartrate is indicated for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer, metastatic breast cancer, and other types of cancer as determined by a physician.
Dosage and Administration: It is typically administered intravenously as a single agent or in combination with other anticancer drugs. The dosage and schedule are determined by the physician based on factors such as the patient's height, weight, general health, and type of cancer being treated.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



