- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 93793-83-0
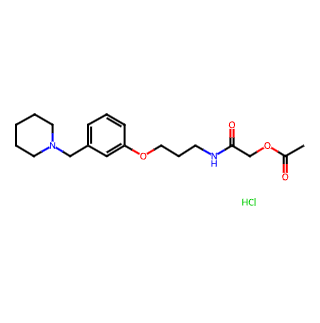



Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride
Basic Information:
Chinese Name: 盐酸罗沙替丁醋酸酯
English Name: Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride
Alternative Names: HOE 760
Molecular Formula: C19H29ClN2O4
Molecular Weight: 384.8976
Pharmacological Actions:
Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride is an effective, selective, competitive, and orally active histamine H2 receptor antagonist. Its main pharmacological actions include:
Inhibition of Gastric Acid Secretion: It has a significant antisecretory effect on gastric acid secretion, stronger than cimetidine and ranitidine.
Suppression of Inflammatory Responses: By inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK, it can suppress inflammatory responses and has been studied for use in gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Antitumor Activity: In vivo studies have shown that Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride exhibits tumor growth inhibition.
Clinical Applications:
Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride is primarily used in the treatment of diseases related to excessive gastric acid secretion, such as:
Low-risk patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding caused by peptic ulcers, acute stress ulcers, hemorrhagic gastritis, etc.
Adjunctive therapy for gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Adverse Reactions:
According to literature reports, adverse reactions associated with Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride include:
Hepatic and biliary system disorders, such as elevated AST and ALT levels.
Blood system disorders, including leukopenia and eosinophilia.
Severe adverse reactions include shock, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), hepatic dysfunction, jaundice, rhabdomyolysis, etc.
Precautions:
Patients with a history of drug allergies should avoid use, and caution is advised in patients with impaired liver or renal function and the elderly.
During treatment, close monitoring is essential. The lowest effective dose should be used, and alternative therapy should be considered if treatment is ineffective.
Intravenous administration may cause transient pain at the injection site, necessitating careful attention to the injection site and technique.
The use of this drug may mask the symptoms of gastric cancer; therefore, malignancy should be ruled out before administration.
Drug Interactions:
Currently, there is limited information on the drug interactions of Roxatidine Acetate Hydrochloride, but caution should be exercised regarding potential interaction risks.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



