- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS Number: 22560-50-5



Basic Information
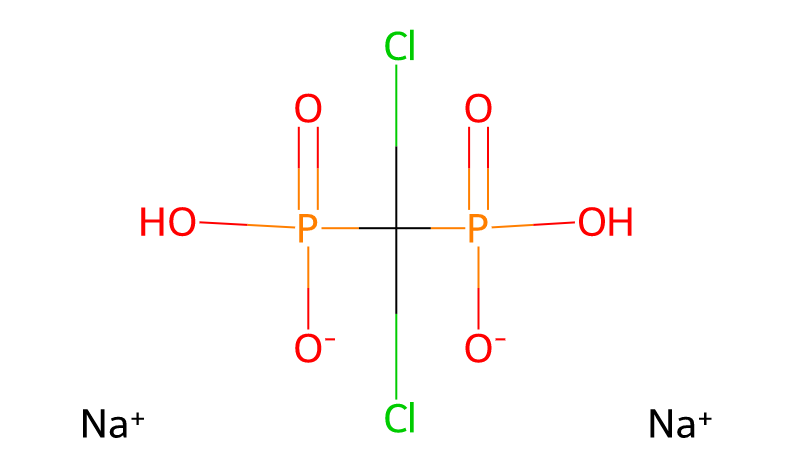
Product Name: Clodronate Disodium
CAS Number: 22560-50-5
Molecular Formula: Varying as CH2Cl2Na2O6P2 and CH5Cl2NaO6P2 (likely due to different forms or salts)
Molecular Weight: Varying as 288.85 g/mol and 268.88 g/mol (ditto)
Common Names: Disodium Chlorophosphate, ATP-ADP Transporter Inhibitor
Physical Properties
Appearance: White to off-white solid powder
Solubility: Highly soluble in water, with a solubility of 10 mg/ml in PBS (pH 7.2); practically insoluble in ethanol (96%), slightly soluble in methanol
Melting Point: Above 330°C
Density: Mentioned as 2.306 g/cm3 in some sources (may vary depending on form or conditions)
Boiling Point: 474.7°C at 760 mmHg
Flash Point: 240.9°C
Chemical and Biological Properties
Chemical Properties: Clodronate Disodium is a non-nitrogenous bisphosphonate that binds to hydroxyapatite crystals with an affinity constant of 0.72 µM, inhibiting their growth (IC50=1.34µM) and bone resorption. Inside cells, it can be metabolized to a β-γ-methylene analog of ATP.
Biological Activities:
Anti-osteolytic Effects: Clodronate Disodium is an effective anti-osteolytic agent that inhibits bone resorption. It specifically binds to hydroxyapatite in bone and inhibits osteoclast activity.
Cytotoxicity: It exhibits cytotoxicity towards osteoclasts and macrophages, which belong to the same cellular lineage as osteoclasts. Liposome-encapsulated bisphosphonates, such as clodronate, have been used in biological research to selectively deplete macrophage-like cells and cancer cells.
Induction of Apoptosis: Clodronate Disodium can induce apoptosis in osteoclasts in vitro and in peritoneal macrophages in vivo in mice when administered in liposomes.
Uses and Clinical Applications
Uses: As the first-generation bisphosphonate for osteoporosis treatment, Clodronate Disodium is widely used in the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease of bone, hypercalcemia, and bone pain caused by metastatic bone tumors.
Clinical Applications: In clinical practice, Clodronate Disodium is administered as tablets or injections to control hypercalcemia, osteolysis, and other symptoms associated with malignant tumors. It can also be used to prevent or delay osteolytic bone metastases in malignant tumors.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



