- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
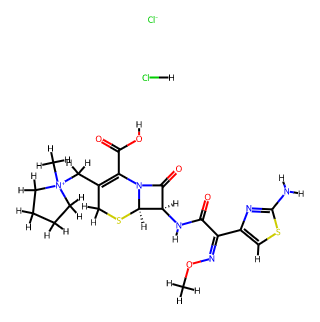
CAS Number: 107648-80-6



I. Basic Information
Chemical Formula: C19H26Cl2N6O5S2
Molecular Weight: 553.483
CAS Registry Number: 107648-80-6
Melting Point: 150°C (decomposes)
Appearance: White to pale yellow powder, odorless or slightly characteristic odor. Soluble in water or methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol, practically insoluble in ether.
II. Pharmacological Properties
Category: Hydrochloride Cefepime is a broad-spectrum fourth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal action by inhibiting the biosynthesis of bacterial cell walls.
Antibacterial Spectrum: It acts against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Specifically, it has low affinity for β-lactamases encoded by bacterial chromosomes, is highly resistant to hydrolysis by most β-lactamases, and can rapidly penetrate into the cells of Gram-negative bacteria. Within bacterial cells, its target molecule is penicillin-binding protein (PBP).
Indications: It is used to treat moderate to severe infections caused by sensitive bacteria in adults and children aged 2 months to 16 years, including lower respiratory tract infections (pneumonia and bronchitis), uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infections (including pyelonephritis), uncomplicated skin and skin soft tissue infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections (including peritonitis and biliary infections), gynecological and obstetrical infections, sepsis, and empirical treatment of febrile neutropenia. It can also be used in pediatric bacterial meningitis.
III. Pharmacokinetic Properties
Absorption: After intramuscular administration, Cefepime hydrochloride is completely absorbed, with a peak plasma concentration (tmax) of approximately 1.5 hours.
Distribution: The average steady-state volume of distribution of Cefepime is 18.0±2.0 liters. Therapeutic concentrations can be achieved in urine, bile, peritoneal fluid, vesicular fluid, tracheal mucosa, sputum, prostate fluid, appendix, gallbladder, and it can cross the inflamed blood-brain barrier.
Excretion: Cefepime and its metabolites are mainly excreted renally, with approximately 85% of the administered dose of Cefepime hydrochloride excreted unchanged in the urine.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



