- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 541-15-1



Basic Information
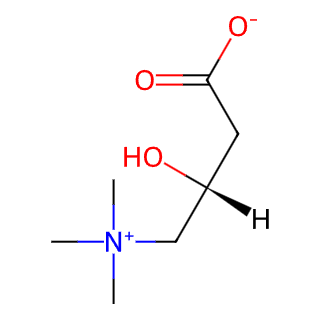
English Name: Levocarnitine
Synonyms: L-Carnitine, Vitamin BT, 3-Hydroxy-4-(trimethylammonio)-butanoate
CAS Number: 541-15-1
Molecular Formula: C7H15NO3
Molecular Weight: 161.20 g/mol
Pharmacological Action
Levocarnitine plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fatty acids and helps convert them into energy in the following ways:
1. Fatty Acid Transport:
o Levocarnitine is essential for the transport of long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane, where they undergo β-oxidation to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
2. Energy Production:
o By facilitating the transport and subsequent oxidation of fatty acids, Levocarnitine is integral in sustaining energy production, particularly in tissues with high energy demands like muscles and the heart.
3. Ammonia Detoxification:
o Levocarnitine helps in detoxifying excess ammonia in the body by forming acetylcarnitine, which enhances the excretion of ammonia, thus aiding in urea cycle disorders.
4. Peripheral Neuropathy:
o It may improve symptomatic relief in patients with peripheral neuropathy, particularly in conditions like diabetic neuropathy and neuropathies due to chronic renal failure.
5. Carnitine Deficiency:
o Levocarnitine supplementation is indicated in primary and secondary carnitine deficiency, ensuring proper fatty acid catabolism and energy production.
6. Cardioprotection:
o It may provide protective effects in cardiac diseases by improving cardiac metabolism and reducing oxidative stress-related damage.
7. Muscle Metabolism:
o Levocarnitine assists in improving muscle metabolism and function, which can be particularly beneficial for athletes and patients suffering from muscle fatigue and weakness.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



