- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 1069-66-5



Basic Information
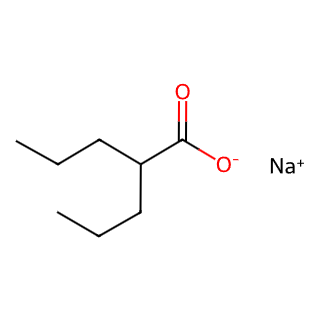
English Name: Sodium Valproate
Synonyms: Valproate sodium, Depakote, Epilim, Convulex
CAS Number: 1069-66-5
Molecular Formula: C8H15NaO2
Molecular Weight: 166.19 g/mol
Pharmacological Actions
Sodium Valproate (Valproic acid sodium salt) is a well-known anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder. It is also used to prevent migraine headaches. Here are some of its key pharmacological actions:
1. Enhanced GABAergic Activity: Sodium Valproate increases the levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain by inhibiting GABA transaminase, an enzyme responsible for GABA breakdown. Increased GABAergic activity contributes to its anticonvulsant effects by inhibiting neural excitability.
2. Reduction of Excitatory Transmission: It inhibits the voltage-gated sodium channels, which decreases the repetitive firing of neurons. This stabilization of neuronal membranes also helps in seizure control.
3. Mood Stabilization: While the precise mechanism is unclear, it's believed that the mood-stabilizing effects could be due to its influence on neurotransmitter systems, neuroprotection, and inhibition of enzyme activities like histone deacetylases.
4. Alteration of Inositol Metabolism: Sodium Valproate impacts the phosphoinositide signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in mood regulation and neuroprotection.
5. Neuroprotective Effects: It shows protective properties against neurotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in neuronal cells.
6. Modulation of Ion Channels: Apart from sodium channels, it affects other ion channels like calcium channels, contributing to its broad-spectrum antiepileptic activities.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



