- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
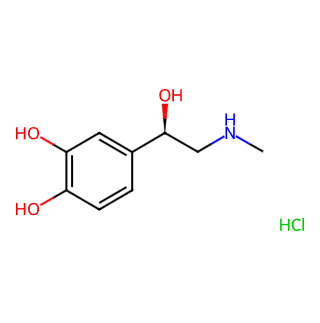
CAS NO.: 55-31-2



Basic Information
Chemical Name: (-)-α-(methylamino)ethanol (+)-bitartrate monohydrate hydrochloride
CAS Number: 55-31-2
Molecular Formula: C9H13NO3•HCl (Actual molecular formula for epinephrine may vary slightly depending on the salt form)
Molecular Weight: Approximate, as the exact weight depends on the salt form
Physical Properties
Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol, but insoluble in chloroform and ether. Forms water-soluble salts easily with dilute hydrochloric acid. Its aqueous solutions decompose to red upon exposure to light or air.
Stability: Unstable in neutral or alkaline aqueous solutions, prone to oxidation and degradation. Storage requires cool, well-ventilated conditions, separate from foodstuffs.
Pharmacological Effects
Cardiovascular System: A potent cardiovascular agent, it stimulates β-receptors in the myocardium, conduction system, and sinoatrial node, enhancing myocardial contractility, cardiac output, conduction velocity, and heart rate. Additionally, it activates α-receptors in skin, mucous membranes, and visceral vessels, causing vasoconstriction and elevating blood pressure.
Respiratory System: Stimulates β2-receptors in the bronchi, dilating them and aiding in the management of respiratory diseases like asthma.
Metabolic System: Acts on hepatic and adipose β2-receptors, promoting glycogenolysis and lipolysis, thereby raising blood glucose levels.
Clinical Applications
Cardiac Emergencies: Widely used in emergency resuscitation for cardiac arrest, helping restore cardiac function and elevate blood pressure, promoting circulation.
Anaphylactic Shock: Effective in treating anaphylactic shock, rapidly alleviating symptoms.
Other Allergic Conditions: Such as bronchial asthma and urticaria, it can also be used in the management of these conditions.
Local Hemostasis: When combined with local anesthetics, it aids in local hemostasis and prolongs the anesthetic effect. In surgical and traumatic procedures, it constricts blood vessels, reducing bleeding and aiding in the control of bleeding sites.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



