- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 85650-52-8



Chemical Basic Information
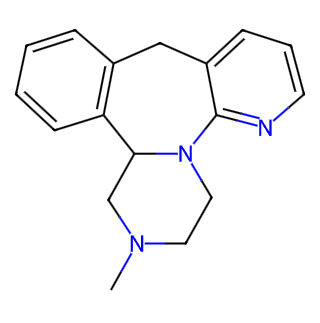
English Name: Mirtazapine
Chemical Name: 1,2,3,4,10,14b-Hexahydro-2-methylpyrazinol[2,1-a]pyrido[2,3-c]benzazepine
Molecular Formula: C17H19N3
Molecular Weight: 265.353
CAS Number: 85650-52-8
Pharmacological Actions
1. Noradrenergic and Serotonergic Effects:
Mirtazapine, as a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSA), works by blocking central presynaptic alpha-2 receptors. This enhances adrenergic neurotransmission, increasing the release of noradrenaline. Similarly, Mirtazapine interacts with central serotonin (5-HT2 and 5-HT3) receptors, modulating serotonin function, and enhancing its release and transmission.
2. Receptor Antagonism:
Mirtazapine is a 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, which can block adverse effects mediated by these receptors following the increase of serotonin, such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, agitation, nervousness, and insomnia. It also antagonizes histamine H1 receptors and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, but with lower affinity, resulting in fewer adverse effects.
3. Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects:
Mirtazapine enhances the release of noradrenaline and 5-HT1A-mediated serotonergic transmission, providing antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. It is effective in ameliorating symptoms such as anhedonia, psychomotor retardation, poor sleep (early awakening), and weight loss.
4. Sedative Effects:
Mirtazapine is well-tolerated, with negligible anticholinergic effects and no impact on the cardiovascular system at therapeutic doses. It offers sedative effects that can improve the quality of sleep in patients.
5. Metabolism and Excretion:
Mirtazapine undergoes metabolism in the liver via CYP2D6, producing desmethylmirtazapine, which also has antidepressant activity. It is primarily excreted through urine and feces. Impaired liver and kidney function can lead to reduced clearance of the drug.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



