- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 134523-00-5
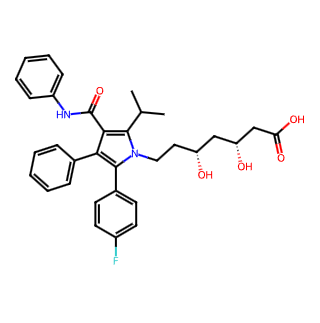



Basic Information
English Name: Atorvastatin
CAS Number: 134523-00-5
Molecular Formula: Depending on the form, it can be C33H35FN2O5 for the free acid form or C66H68CaF2N4O10 for the calcium salt form.
Molecular Weight:
Free acid form: approximately 558.64 g/mol
Calcium salt form: 1155.34 g/mol
Physical Properties
Melting Point: 176-178°C (approximately)
Boiling Point: ~722°C (predicted)
Density:
Free acid form: approximately 1.23 g/cm³ (predicted)
Calcium salt form: 1.236 g/cm³ (measured)
Chemical Properties
Atorvastatin is a lipid-lowering medication that works by inhibiting the activity of HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme essential for cholesterol synthesis. This results in decreased production of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides.
It has various synonyms and aliases that reflect its chemical structure and functional characteristics, such as Atorvastatin Acid and Atorvastatin Hemicalcium.
Uses and Synthesis
Atorvastatin is primarily used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia. It can also be employed in the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease and cerebral stroke.
Its synthesis typically involves intricate organic chemical reactions, including reduction, hydrolysis, acidification, and other steps, ultimately yielding Atorvastatin or its salt forms.
Safety Information
When handling Atorvastatin, it is crucial to prioritize safety measures such as avoiding contact with eyes, skin, and inhalation of its dust.
In case of accidental contact, immediate rinsing with copious amounts of water and seeking medical attention is advised.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



