- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 32780-64-6
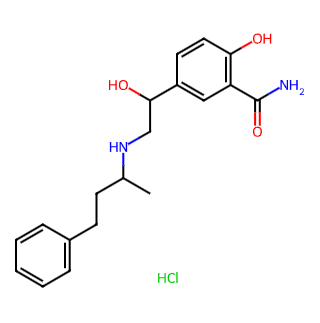



Labetalol Hydrochloride is an essential pharmaceutical compound primarily used in the treatment of hypertension, particularly hypertensive disorders complicating pregnancy. Below is a detailed analysis of Labetalol Hydrochloride:
I. Basic Information
English Name: Labetalol Hydrochloride
Alternative Names: Trandate, Normodyne, 2-Hydroxy-5-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl)amino]ethyl]benzamide Hydrochloride
CAS Number: 32780-64-6
Molecular Formula: C19H25ClN2O3
Molecular Weight: 364.87 g/mol
EINECS Number: 251-211-1
II. Physical and Chemical Properties
Melting Point: Approximately 187-189°C
Solubility: Soluble in water
Storage Conditions: Recommended storage temperature of 2-8°C
III. Pharmacological Effects
Labetalol Hydrochloride possesses both alpha and beta receptor blocking actions with weak intrinsic activity and membrane-stabilizing properties.
Its beta receptor blocking effect is approximately 4-8 times that of its alpha receptor blocking effect, with a beta1 receptor blocking effect roughly one-fourth that of propranolol and a weaker beta2 receptor blocking effect.
By blocking beta receptors while simultaneously exerting a vasodilatory effect through blocking alpha receptors, it contributes to its antihypertensive and anti-anginal mechanisms.
Compared to pure beta blockers, Labetalol Hydrochloride exhibits stronger hypotensive effects during standing and exercise tests and increases renal blood flow.
IV. Indications
Indications: Suitable for the treatment of mild to severe hypertension and angina pectoris; intravenous administration can treat hypertensive crises, particularly in hypertensive pregnant women or those with preeclampsia, pheochromocytoma, malignant hypertension, and hypertensive crises.
V. Safety Information
Hazard Symbol: Xn (Harmful)
Risk Phrase: R22 (Harmful if swallowed)
Safety Phrase: S36 (Wear suitable protective clothing)
In summary, Labetalol Hydrochloride, as an important antihypertensive drug, has broad prospects and significant value in clinical applications.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



