- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 91503-79-6
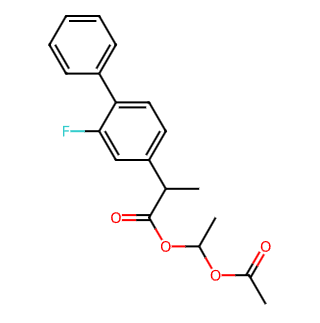



Flurbiprofen Axetil
Flurbiprofen Axetil is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used primarily for targeted postoperative pain relief and the management of cancer-related pain.
Basic Information
Generic Name: Flurbiprofen Axetil
CAS No.: 91503-79-6
Molecular Formula: C19H19FO4
Molecular Weight: 330.36
Pharmacological Effects
Flurbiprofen Axetil exhibits multiple therapeutic effects, including analgesia, antipyresis, anti-inflammation, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and reduction of fibrinogen concentrations.
Analgesia: It blocks the P-substance receptors in the nerve conduction pathway, thereby reducing the transmission of pain signals induced by noxious stimuli. Additionally, it inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) in the spinal cord and periphery, leading to a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which helps alleviate pain hypersensitivity caused by surgical trauma or other causes.
Antipyresis: By inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center, it reduces fever.
Anti-inflammation: Inhibition of COX activity in the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway reduces the production of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins, mitigating tissue edema and erythema.
Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation: It interferes with platelet activation processes by affecting intracellular calcium concentrations.
Reduction of Fibrinogen Concentrations: By influencing the activity of coagulation factor Xa, it disrupts the coagulation process.
Clinical Applications
Flurbiprofen Axetil injection has a wide range of clinical applications, primarily for postoperative pain relief and cancer pain management. Its advantages include no central nervous system depression, allowing for immediate use after surgery without affecting the patient's arousal state. Additionally, it regulates the cytokine response by inhibiting excessive stress reactions caused by surgical trauma, maintaining a balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which is crucial for postoperative recovery.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



