- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 51110-01-1
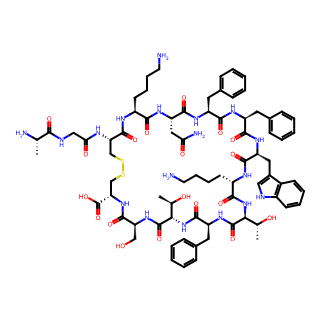



Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH), is a peptide hormone secreted by the hypothalamus and D-cells of the gastrointestinal mucosa, among other sources. It exhibits a multitude of physiological functions.
Basic Information
English Name: Somatostatin
CAS No.: 51110-01-1
Molecular Formula: C76H104N18O19S2
Molecular Weight: 1637.88
Chemical Characteristics
Somatostatin is a polypeptide hormone consisting of multiple amino acid residues in its molecular structure.
Within the gastrointestinal tract, somatostatin is primarily released by D-cells as a 14-amino acid peptide.
Physiological Functions
Inhibits Growth Hormone Release: Somatostatin regulates growth and development by inhibiting the release of growth hormone (GH) from the anterior pituitary gland.
Suppresses Insulin and Glucagon Secretion: It exerts a direct inhibitory effect on pancreatic beta-cells, suppressing insulin secretion, and also inhibits glucagon secretion.
Reduces Gastric Acid Secretion and Gastrointestinal Motility: Through paracrine mechanisms, somatostatin potently inhibits gastric acid secretion. It also modulates gastrointestinal smooth muscle contractility, slowing down gut motility.
Other Roles: Somatostatin influences the release of other hormones, regulates immune system functions, and participates in stress responses, among other physiological effects.
Clinical Applications
Due to its diverse physiological actions, somatostatin or its analogs hold promising clinical applications. For instance, they may have therapeutic potential in treating certain endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, and even cancer.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



