- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 57-83-0
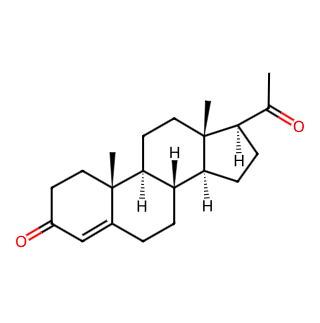



Progesterone
Progesterone is a vital hormone in females, also known as the progestogen or progesterone hormone.
I. Basic Information
English Name: Progesterone
Molecular Formula: C21H30O2
Molecular Weight: 314.46
CAS Registry Number: 57-83-0
II. Physiological Functions
Supporting Pregnancy:
During pregnancy, progesterone is secreted in significant amounts by the corpus luteum of the ovary and the placenta, aiding in maintaining the continuation of gestation.
It helps reduce uterine excitability, inhibiting uterine contractions, and protecting the fetus by creating a stable environment for its development.
Regulating Menstrual Cycle:
In non-pregnant women, progesterone is mainly secreted by the corpus luteum in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, participating in regulating the menstrual cycle.
It prepares the endometrium for implantation by thickening it, and if pregnancy does not occur, it contributes to the shedding of the endometrium during menstruation.
Promoting Breast Development:
Progesterone, along with estrogen, promotes the development of mammary glands, preparing them for lactation.
Influencing Metabolism:
Progesterone plays a role in regulating carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism in females.
Other Functions:
It also helps in reducing body temperature and regulating water-salt balance.
III. Clinical Applications
Treating Menstrual Disorders:
Progesterone-based medications can be used to treat menstrual disorders such as amenorrhea and dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Preventing Miscarriage:
In early pregnancy, low progesterone levels may increase the risk of miscarriage. Therefore, doctors may prescribe progesterone supplements to help prevent it.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
Progesterone is used extensively in ART procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) to enhance pregnancy success rates.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



