- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 86541-74-4



Basic Information
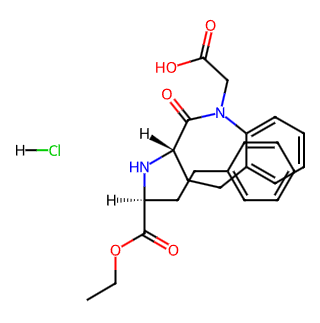
English Name: Benazepril Hydrochloride
CAS Number: 86541-74-4
Molecular Formula: C24H29ClN2O5
Molecular Weight: 460.95 (may vary slightly depending on sources, e.g., 460.955 or 460.951)
Physical and Chemical Properties
Melting Point: 188-190°C
Boiling Point: 691.2°C at 760 mmHg
Appearance: Crystalline solid
Solubility: Soluble in DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), with a solubility of approximately 34 mg/mL
Storage Conditions: Dry and preferably stored at +4°C
Chemical Properties
Benazepril Hydrochloride is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI). Upon oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed and converted to its active metabolite, benazeprilat. By inhibiting the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme, it reduces the formation of angiotensin II, thereby lowering blood pressure, reducing cardiac load, and improving cardiac function.
Uses
Benazepril Hydrochloride is primarily used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. It can also serve as an adjunctive therapy for patients with congestive heart failure who are not adequately responsive to digitalis and/or diuretics.
Safety Information
Risk Phrases:
S22: Do not breathe dust.
S24/25: Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
UN Number (for transportation of dangerous goods): 3077 (however, note that Benazepril Hydrochloride may not be classified as a dangerous good according to some sources)
First Aid Measures:
If inhaled, move the patient to fresh air.
If contact with skin or eyes occurs, flush with plenty of water.
If swallowed, seek medical attention immediately.
Precautions
When using Benazepril Hydrochloride as a medication, follow medical advice regarding dosage and timing. Patients with allergies or a history of specific diseases should use it cautiously under physician supervision.
In summary, CAS NO. 86541-74-4 represents Benazepril Hydrochloride, a vital pharmaceutical intermediate and active ingredient known for its significant antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



