- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 137862-53-4
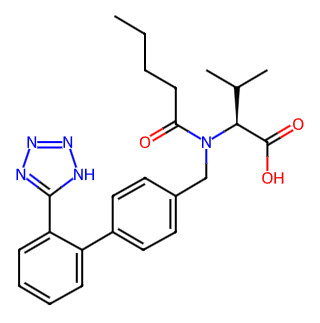



Valsartan, also known as Diovan, is a widely used antihypertensive medication belonging to the class of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
Basic Information
Generic Name: Valsartan
Alternative Names: Diovan, Valxartan, etc.
CAS Number: 137862-53-4
Molecular Formula: C24H29N5O3
Molecular Weight: 435.51900
Pharmacological Action
Valsartan works by blocking the binding of angiotensin II (Ang II) to the AT1 receptor, thereby inhibiting the vasoconstrictive and aldosterone-releasing effects of Ang II. This mechanism contributes to the reduction of blood pressure, which in turn eases the burden on the heart and blood vessels, improving cardiovascular health.
Clinical Applications
Hypertension Treatment: Valsartan is a key medication in the management of hypertension, particularly suitable for patients who are intolerant to ACE inhibitors.
Heart Failure: It is also indicated for the treatment of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction, improving survival rates and quality of life for patients.
Combination Therapy: For patients with hypertension that cannot be controlled with a single medication, valsartan is often used in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, such as diuretics, to enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Drug Characteristics
Stability: Valsartan offers a sustained and stable antihypertensive effect.
Toxicity and Side Effects: It has relatively low toxicity and good tolerability in patients.
Synthesis and Storage
Valsartan is produced through a complex chemical synthesis process designed to efficiently construct its specific chemical structure while ensuring product purity and stability. It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



