- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS Number: 120511-73-1



Basic Information
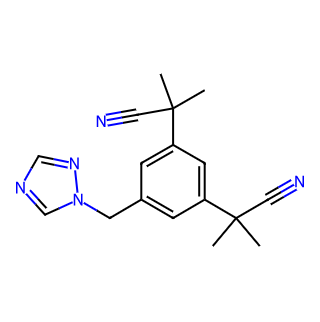
Product Name: Anastrozole
CAS Number: 120511-73-1
Chemical Formula: C17H19N5
Molecular Weight: 297.37 g/mol
Physical Properties
Appearance: White or almost white crystalline powder, odorless, bitter taste.
Solubility: Easily soluble in acetonitrile or ethyl acetate, soluble in ethanol, practically insoluble in water. In cellular experiments, the solubility in DMSO is ≥100 mg/mL (340.87 mM; note that hygroscopic DMSO significantly affects the solubility of the product, and freshly opened DMSO should be used).
Chemical and Biological Activity
Mechanism of Action: Anastrozole is a selective inhibitor of aromatase, reducing estrogen synthesis by inhibiting the activity of placental aromatase. It has an IC50 value of 15 nM, indicating strong inhibitory effects.
In Vitro Studies: In vitro, Anastrozole inhibits aromatase activity 200 times more potently than aminoglutethimide (AG), twice as potently as 4-OHA, and one-third as potently as Fadrozole.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution: Anastrozole is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a time to maximum plasma concentration (tmax) of 2 hours on an empty stomach. It is eliminated slowly, with a plasma half-life of approximately 40-50 hours.
Metabolism and Excretion: Anastrozole is extensively metabolized in vivo. After dosing, the primary radioactive component in plasma is Anastrozole. After 72 hours, metabolite concentrations increase to equal those of Anastrozole. Within 72 hours, less than 10% of the dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug. Metabolism includes N-dealkylation, hydroxylation, and glucuronidation, with metabolites primarily excreted in urine and minimally in feces.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



