- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 51481-61-9
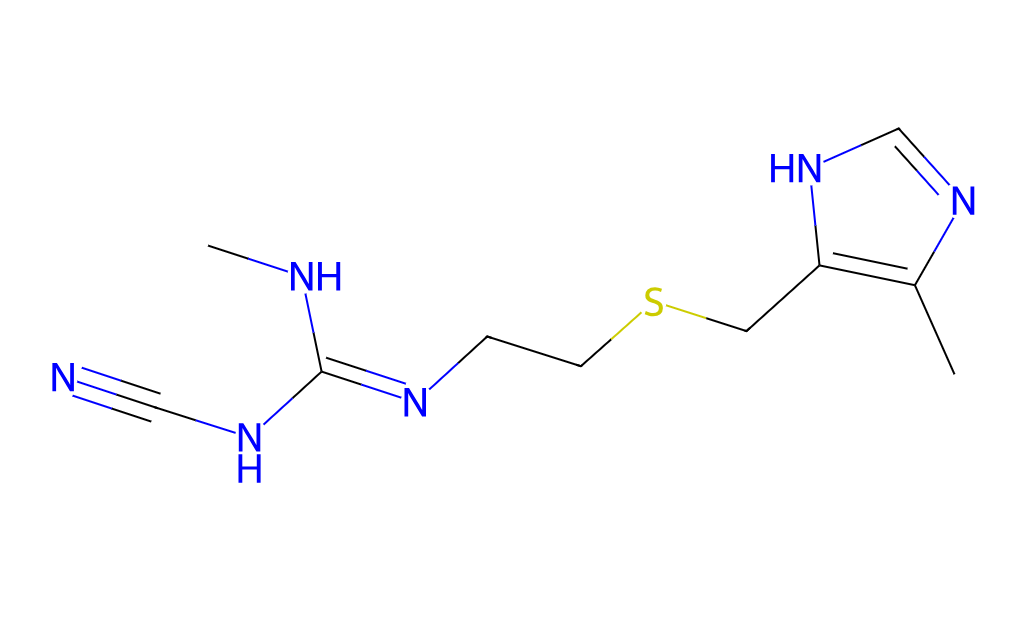



Chemical Information
English Name: Cimetidine
Molecular Formula: C10H16N6S
Molecular Weight: 252.34 g/mol
CAS Number: 51481-61-9
Pharmacological Action
1. Histamine H2 Receptor Antagonist:
o Mechanism of Action: Cimetidine works by competitively inhibiting the histamine H2 receptors found on the basolateral membrane of parietal cells in the stomach lining. This action reduces the production of gastric acid.
o Therapeutic Use: It is commonly used to treat and prevent ulcers in the stomach and intestines, manage gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and conditions that cause excessive stomach acid secretion, such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
2. Inhibits Gastric Acid Secretion:
o Effect: By blocking the H2 receptors, Cimetidine effectively reduces the volume and concentration of gastric acid, relieving symptoms of heartburn and indigestion.
o Clinical Benefits: This leads to improved healing of ulcers and other gastric mucosal injuries.
3. Increases Gastric pH:
o Outcome: The decrease in gastric acid results in a higher pH level in the stomach, creating a less acidic environment which is conducive for the healing of ulcers and reducing acid reflux symptoms.
4. Secondary Actions:
o Enzyme Inhibition: Cimetidine has been shown to inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes, which can affect the metabolism of various drugs. This property necessitates careful drug interaction considerations when prescribing Cimetidine to patients taking multiple medications.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



