- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS No.: 50-56-6
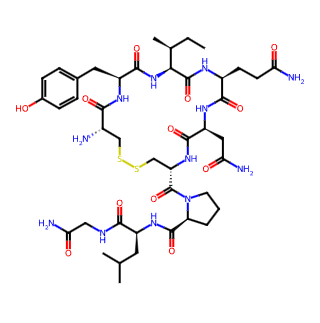



Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary gland and synthesized in the paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus. Composed of nine amino acids, it exhibits a diverse range of physiological functions and effects.
Basic Information
English Name: Oxytocin
Chemical Formula: C43H66N12O12S2
Molecular Weight: 1007.19
CAS Number: 50-56-6
Physiological Functions
Stimulates Uterine Contraction: During childbirth, oxytocin stimulates the contraction of uterine smooth muscle, aiding in the expulsion of the fetus.
Promotes Lactation: It stimulates the secretion of milk from the mammary glands, crucial for breastfeeding.
Enhances Maternal Bonding: Studies suggest that oxytocin strengthens the emotional bond between mother and infant, fostering maternal love.
Lowers Blood Pressure: By reducing levels of stress hormones like adrenaline, oxytocin contributes to lowering blood pressure.
Regulation of Secretion
Oxytocin secretion is regulated by various factors, including neural and humoral mechanisms. Increased estrogen levels during pregnancy and childbirth enhance oxytocin synthesis and release. Additionally, inhaling oxytocin can enhance its physiological effects.
Clinical Applications
Due to its crucial roles in childbirth and lactation, oxytocin is widely used in clinical settings. However, its application is limited as an immature uterus may have low or no responsiveness to oxytocin, while a pregnant uterus nearing childbirth exhibits the highest responsiveness.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



