- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 1319-82-0
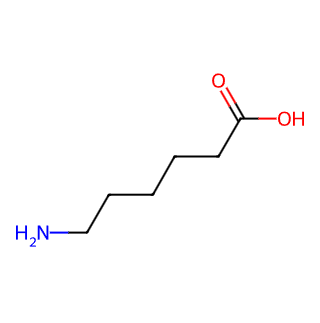



Aminocaproic Acid (CAS No. 1319-82-0)
Aminocaproic Acid, identified by its Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) number 1319-82-0, is a crucial medicinal compound with a wide array of applications in the medical and pharmaceutical fields.
Basic Information
CAS Number: 1319-82-0
Chemical Name: Aminocaproic Acid
Common Names: 6-Aminocaproic Acid, ε-Aminocaproic Acid
Chemical Formula: C6H13NO2
Molecular Weight: Calculated based on the chemical formula (not directly stated in the reference)
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Purity: Typically 98% to 99% or higher, depending on the manufacturer and intended use
Physical Properties
Density: 1.042 (may vary under different conditions)
Melting Point: 205-207°C
Boiling Point: 255.6°C at 760 mmHg
Refractive Index: 1.465
Polar Surface Area (PSA): 63.32000
LogP (Octanol-Water Partition Coefficient): 1.29040
Solubility: Soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, practically insoluble in chloroform or ether
Pharmacological Effects
Aminocaproic Acid is a specific antifibrinolytic agent that functions primarily by:
Inhibiting the Activation of Plasminogen: Preventing the conversion of plasminogen into plasmin, thereby blocking the fibrinolytic process.
Direct Inhibition of Plasmin: At high concentrations, it can also directly inhibit plasmin activity, enhancing its hemostatic effects.
Clinical Applications
Due to its pharmacological properties, Aminocaproic Acid is used in various clinical settings, including:
Surgical Hemostasis: Reducing postoperative bleeding and promoting wound healing in cardiovascular, orthopedic, and transplant surgeries.
Obstetric and Gynecological Bleeding: Managing postpartum hemorrhage, miscarriage bleeding, and other obstetrical and gynecological bleeding situations.
Other Bleeding Conditions: Treating pulmonary hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, and other bleeding disorders.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



