- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 13292-46-1
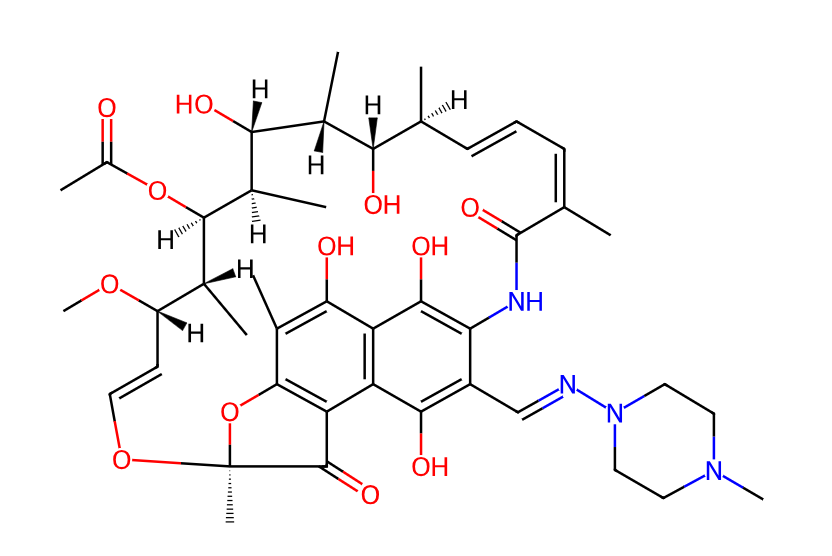



Rifampicin, a crucial semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic, is primarily used in the treatment of tuberculosis and other infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Basic Information
Product Name: Rifampicin (Abbreviated as RFP)
CAS Number: 13292-46-1
Molecular Formula: C43H58N4O12
Molecular Weight: 822.94 (some sources may list it as 822.95, but the difference is minimal due to rounding or precision)
Physical Properties
Appearance: Rifampicin is typically an orange-red crystalline powder or brick-red crystals. It is light-sensitive and prone to degradation upon exposure to light.
Solubility: Highly soluble in DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) and methanol, slightly soluble in water.
Chemical Properties
Stability: Rifampicin should be stored and used under light-protected conditions due to its sensitivity to light.
Reactivity: Rifampicin exerts its antibacterial effect by strongly binding to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting its activity, and thereby blocking bacterial RNA synthesis.
Pharmacological Properties
Antibacterial Spectrum: Rifampicin possesses a broad antibacterial spectrum, demonstrating potent activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae, atypical mycobacteria, and a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Mechanism of Action: By inhibiting the bacterial RNA polymerase, specifically the β-subunit of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, Rifampicin disrupts the initiation phase of bacterial RNA synthesis, ultimately inhibiting bacterial growth.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



