- Synthetic anti-infective drugs
- Medications for the digestive system
- Antipyretic and analgesic drugs
- Medications for the blood system
- Medications for the respiratory system
- Anti-allergic drugs
- Medications for the urinary system
- Diagnostic medications
- Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory drugs
- Vitamins and mineral supplements
- Antioxidants and medications for osteoporosis
- Antiparasitic drugs
- Ophthalmic medications
- Amino acids and their derivatives
- Dermatological medications
- Medications for the circulatory system
- Antitumor drugs
- Medications for the nervous system
- Hormonal and endocrine function-regulating drugs
- Antibiotics
- Others
CAS NO.: 128270-60-0
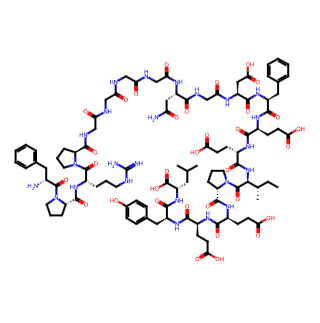



Bivalirudin
Bivalirudin is a synthetic anticoagulant drug, primarily composed of a 20-peptide analog of hirudin. The following provides a detailed introduction to Bivalirudin:
Basic Information
English Name: Bivalirudin
Chemical Name: D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-glycyl-glycyl-glycyl-glycyl-L-asparaginyl-glycyl-aspartyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-glutamyl-L-glutamyl-L-isoleucyl-L-prolyl-L-glutamyl-L-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine
CAS Number: 128270-60-0
Molecular Formula: C98H138N24O33
Molecular Weight: 2180.28000
Pharmacological Action
Bivalirudin is a direct thrombin inhibitor that specifically binds to both the catalytic site and the anionic exosite of free and clot-bound thrombin, thereby inhibiting thrombin activity in a reversible, transient, and specific manner. This inhibition extends not only to free thrombin but also to thrombin bound to the thrombus and is not neutralized by platelet-released substances.
Indications
Bivalirudin is primarily used as an anticoagulant in adult patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). It is also indicated for the prevention of unstable angina and ischemic complications. In patients with known heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), Bivalirudin serves as an alternative to unfractionated heparin.
Market Availability
Bivalirudin was approved for use in the United States in 2000 and subsequently in Europe and China.
In summary, Bivalirudin is a crucial anticoagulant drug that plays a significant role in PCI procedures.

Tai Yau Street, San Po Kong, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.



